jemand anders
Erfahrenes Mitglied
Hallo,
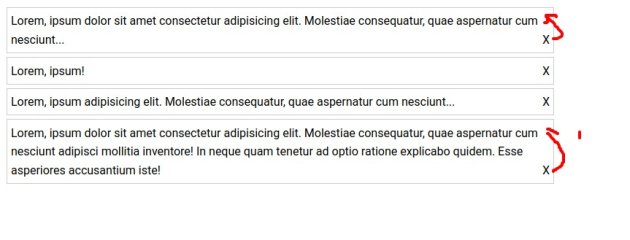
ich möchte eine Information ans eine Ende von Listenelementen anhängen (float:right;content:"x").
Werden die Zeilen jedoch umgebrochen, erscheint die Information jedoch nicht in der obersten Zeile, was logisch sein mag, mir aber optisch nicht gefällt.
Mit einer Ergänzung von position:relative und top:$WERT könnte das Problem umgangen werden.
Allerdings finde ich keine CSS-Lösung, und mit Javascript wird von ComputedStyle immer die Default-Line-Höhe ermittelt, statt der tatsächlichen Höhe.
Im Firefox wird in den Dev-Tools -> Inspector -> Layout jedoch der richtige Wert angezeigt.
Vielleicht hat jemand eine Idee, was ich tun kann, falls es keine Programmmacke ist.
ich möchte eine Information ans eine Ende von Listenelementen anhängen (float:right;content:"x").
Werden die Zeilen jedoch umgebrochen, erscheint die Information jedoch nicht in der obersten Zeile, was logisch sein mag, mir aber optisch nicht gefällt.
Mit einer Ergänzung von position:relative und top:$WERT könnte das Problem umgangen werden.
Allerdings finde ich keine CSS-Lösung, und mit Javascript wird von ComputedStyle immer die Default-Line-Höhe ermittelt, statt der tatsächlichen Höhe.
Im Firefox wird in den Dev-Tools -> Inspector -> Layout jedoch der richtige Wert angezeigt.
Vielleicht hat jemand eine Idee, was ich tun kann, falls es keine Programmmacke ist.
HTML:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="de">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" />
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<!-- check-comp-line-height.html -->
<title>Line Height Computed Value</title>
<style>
body {
max-width: 500px;
}
li {
border: 1px solid #ccc;
line-height: 1.6em;
margin: 5px;
padding: 5px;
list-style-type: none;
}
li:first-child {
overflow: visible;
width: 2000px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>
Lorem, ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Molestiae
consequatur, quae aspernatur cum nesciunt adipisci mollitia inventore!
In neque quam tenetur ad optio ratione explicabo quidem. Esse asperiores
accusantium iste!
</li>
<li>
Lorem, ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Molestiae
consequatur, quae aspernatur cum nesciunt adipisci mollitia inventore!
In neque quam tenetur ad optio ratione explicabo quidem. Esse asperiores
accusantium iste!
</li>
</ul>
<script>
(() => {
const li = document.querySelectorAll("li");
li.forEach((l, idx) => {
let compValue =
"<br/><strong>Computed Value Line Height: " +
window.getComputedStyle(l).getPropertyValue("line-height") +
"</strong>";
document.querySelector(`li:nth-child(${idx + 1})`).innerHTML +=
compValue;
});
})();
</script>
</body>
</html>